The 58th Session of International Astronautical Congress (IAC)
September 24-28, 2007
Hyderabad, India
OPTIMIZATION OF INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC OPTICAL NETWORK FOR GOALS OF OBSERVATIONS OF DIFFERENT SPACE OBJECTS
Igor Molotov, Vladimir Agapov
Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics
IAC-07- A6.1.2
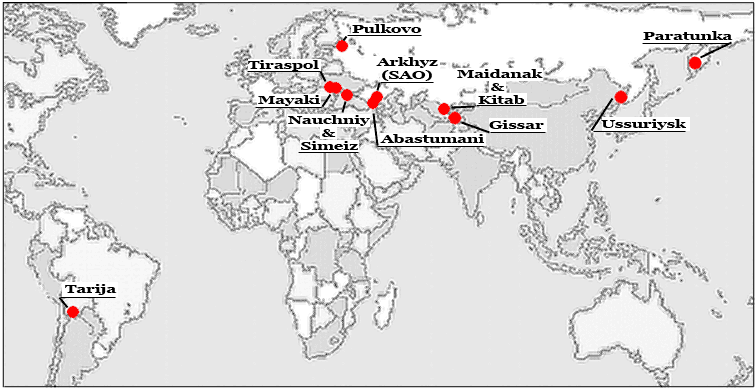
INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC OPTICAL NETWORK (ISON)
- Team of FSU astronomers and ballistics coordinated by the KIAM RAS
- 9 observing facilities working on a regular basis (Nauchny, Ussuriysk, Maidanak, Kitab, Abastumani, Pulkovo, Mayaki, Tiraspol, Tarija)
- 4 facilities collaborating periodically (Mondy, Simeiz, Terskol, Arkhyz (SAO))
- 2 new points are in development (Paratunka, Gissar)
- Small groups on management, technical support, software elaboration, measurements scheduling and processing, optics production, mounts production
Team of the Astronomical Institute of the University of Bern supporting Zimmerwald (AIUB) and Teide (ESA) observatories is in a good cooperation with ISON
New facility of the ISON in Paratunka, Kamchatka
 |
 |
 |
 |
AMC-11 28252/2004-017A, 131.0°W is visible both from Paratunka and Tarija |
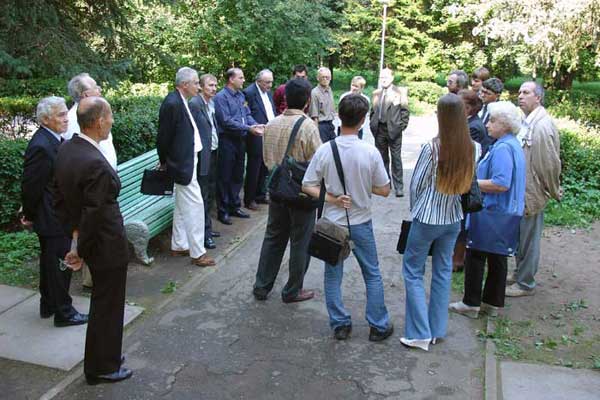
First meeting of the ISON Aug. 2005 Pulkovo
2th meeting of the ISON Jan. 2007 Zvenigorod
Reasons for optimization
- In the beginning, the ISON had the old astrophysical telescopes with different but limited capabilities, which were used for study of all kinds of the space objects
- Their current capacity is not enough for the development and support of the comprehensive space objects database
- Unknown faint objects discovery rate exceeds our ability to track them all at the same time
- For HEO objects tracking dedicated telescopes are required
Therefore the program of telescope modernization and production of new ones is proposed Forming four telescope subsystems
- Creation of subsystem for regular surveying of the GEO and partially HEO objects down to 15m (22-cm telescopes with FOV 4° in Pulkovo, Nauchny, Tiraspol, Kitab, Ussuriysk, Paratunka, Tarija, Abastumani)
- Forming of the subsystem for fragments observations down to 18m (production of two 50 cm class and two 40 cm class telescopes with FOV 2°, upgrade of two 80 cm class and two 70 cm class telescopes, enlarging the FOV of AT-64 – up to 2.3° and Zeiss-600 – up to 1°)
- Arranging of cooperation of 1 m – 2.6 m telescopes for observations of fragments down to 20-21m (2.6-m in Nauchny, 2-m in Terskol, 1.6-m in Mondy, 1.5-m in Maidanak, 1-m in Simeiz, Arkhyz, Maidanak, Gissar)
- Creation of subsystem for regular surveying HEO and partially LEO objects (four 15° FOV optical cameras in Ussuriysk, Kitab, Abastumani, Tarija)
22-cm survey telescopes with FOV of 16 sq. deg
 
 
5 telescopes of 22 cm are installed: Nauchny, Ussuriysk, Tiraspol, Pulkovo, Kitab
1 telescope is produced, 4 are in production
Two new 22-cm telescopes in Ussuriysk and Kitab
 |  |  |
 |  |
| 22-cm telescope with FOV 4° is able to obtain measurements for about 400 GEO and HEO objects down to 15.5m per night |
Subsystem for studying fragments down to 18m
80-cm telescope for Mayaki in production
Cooperation for tracking of the fragments down to 21st magnitude
- 2.6-m ZTSh in Nauchny and 2-m Zeiss in Terskol
- 1.6-m AZT-33IK in Mondy and 1.5-m AZT-22 in Maidanak
- 1-m Zeiss-1000 in Simeiz, Arkhyz, Maidanak, Gissar
INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC OPTICAL NETWORK (ISON) IN 2009
- > 30 telescopes from 15 cm to 2.6 m
- Ability to observe all bright (down to 15.5m) GEO-objects along 360 deg arc
- Ability to search, discover and track the faint fragments down to 21m
- Ability to track the most part of HEO-objects brighter than 15.5m
- Limited capability to observe LEO objects
30 сентября 2007
Доклад публикуется с разрешения авторов
|